Showing results 101 - 150 of 220
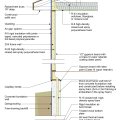
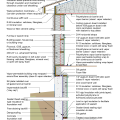
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
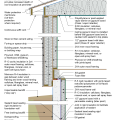
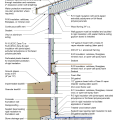
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
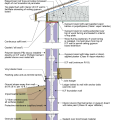
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation
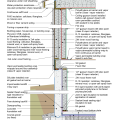
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
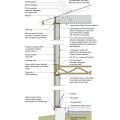
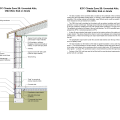
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
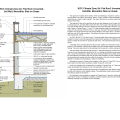
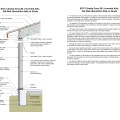
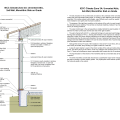
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade
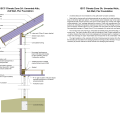
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
A raised wood pier foundation can raise the subfloor above the design flood elevation.
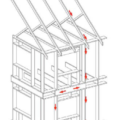
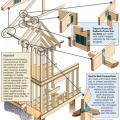
Advanced framing techniques include constructing on a 2-foot grid where wall studs are placed 24 inches on center and aligned with roof and floor trusses for a continuous load path from roof to foundation.
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
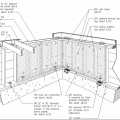
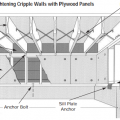
Braced cripple wall construction in crawlspace anchored to framing and foundation
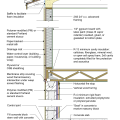
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Brick veneer is supported by a concrete stem wall thermally separated from the slab-on-grade foundation with turn-down footing which is also insulated on top; anchorage for seismic resistance is also shown
Buildings damaged by a hurricane storm surge: upper homes on gulf shoreline were hit by large waves above the lowest floor, lower left home on bay and right school 1.3 miles from gulf shoreline were hit by surge and small waves.
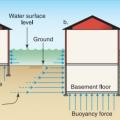
Buoyancy force on dry floodproofed homes with deep basements leads to possible foundation damage
Concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
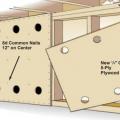
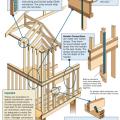
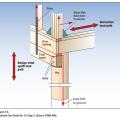
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Correct seismic retrofit hardware for securing the sill plate to foundation wall
Critical connections for providing a continuous load path in buildings and storm shelters
Detail for reinforcing a cripple wall to resist earthquake movement by installing anchor bolts and plywood reinforcement.
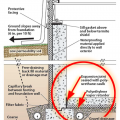
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
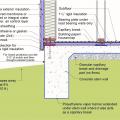
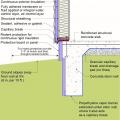
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
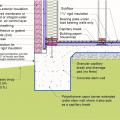
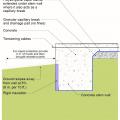
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
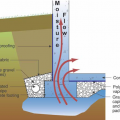
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
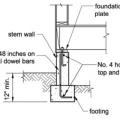
How to properly anchor a new home to its foundation with foundation sill plate, stem wall, and footing
Hurricane straps, hold-down connectors, and bolts help to transfer loads from the building’s walls to its foundation, increasing resistance to vertical and horizontal pressures acting on the building from wind, waves, or ground movement.
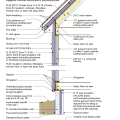
IECC Climate Zone 1A: Unvented Attic with Spray foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall-CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab