Showing results 1 - 21 of 21
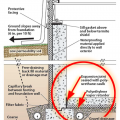
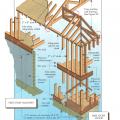
A raised wood pier foundation can raise the subfloor above the design flood elevation.
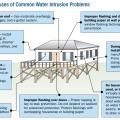
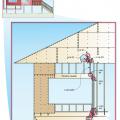
Buildings damaged by a hurricane storm surge: upper homes on gulf shoreline were hit by large waves above the lowest floor, lower left home on bay and right school 1.3 miles from gulf shoreline were hit by surge and small waves.
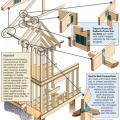
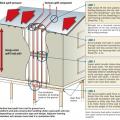
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
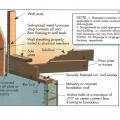
Correct seismic retrofit hardware for securing the sill plate to foundation wall
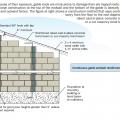
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
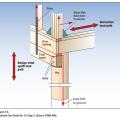
Hurricane straps, hold-down connectors, and bolts help to transfer loads from the building’s walls to its foundation, increasing resistance to vertical and horizontal pressures acting on the building from wind, waves, or ground movement.
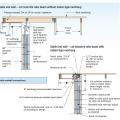
In high wind areas, provide lateral support to masonry end walls to resist high winds.
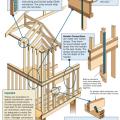
In high-wind regions, special hardware is used for most framing connections; toe-nailing is not acceptable.
Key connection points for a continuous load path for earthquake and high wind disaster resistance
Lower-story wall anchorage to masonry (or concrete) base. Straps properly nailed at wall studs.
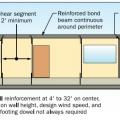
Properly reinforce masonry walls in coastal locations to resist high winds and waves.
Right - A continuous load path connects the roof and wall framing to the foundation.
Right – Examples of wall stud to sill plate and foundation and wall rod connectors and brackets.
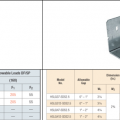
Shear Strength Comparison Between a Foundation Stud Anchor (on left) and a Shear Transfer Angle (on right)
The components of a framed wall include from inside to out: gypsum, wood studs, OSB or plywood sheathing, and siding.
The sheathing has rotted because there was not a sufficient drainage gap behind the stucco cladding