Showing results 1 - 31 of 31
Impervious surfaces like patio slabs, sidewalks, and driveways that are within 10 feet of the home should slope away from the house.
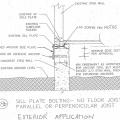
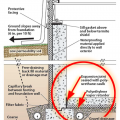
An anchor side plate is used to connect the concrete foundation to the sill plate from the exterior as part of a seismic retrofit when the sill plate is not accessible from the interior of the home
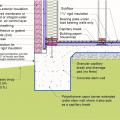
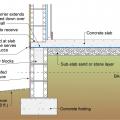
An externally insulated slab-on-grade is pest-protected by a metal termite shield under sill plate, metal-flashing-wrapped foam under siding, a removable inspection strip of PVC-covered foam, and 2 feet of gravel next to the foundation.
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
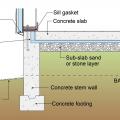
Brick veneer is supported by a concrete stem wall thermally separated from the slab-on-grade foundation with turn-down footing which is also insulated on top; anchorage for seismic resistance is also shown
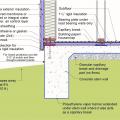
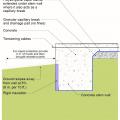
Comprehensive water management features include a capillary break (≥ 6-mil polyethylene sheeting) at all crawlspace floors
Concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
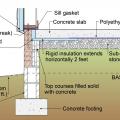
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
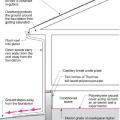
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
Pest protection measures include a termite shield under the rim joist and extending out on either side of the stem wall, insect screening under the furring air gap, and brick veneer to protect slab-edge insulation.
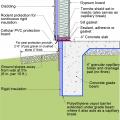
Raised-slab CMU foundation including flood-resistant features: sloped grade, damp proofed stem wall, capillary break under the slab (gravel or sand), vapor barrier under the slab and capillary break at the top of the foundation wall (polyethylene sheet)
Right – The drain slopes away from the foundation and terminates at the proper distance
Right – The raised-slab, brick-and-block stem wall, above-grade walls, and roof of this house use flood damage-resistant materials, integrated water, vapor, and air control layers, and construction methods which promote good drainage and rapid drying
Right – The raised-slab, CMU block stem wall, above-grade walls, and roof of this house use flood damage-resistant materials, integrated water, vapor, and air control layers, and construction methods which promote good drainage and rapid drying
Right – The raised-slab, poured-concrete stem wall, above-grade walls, and roof of this house use flood damage-resistant materials, integrated water, vapor, and air control layers, and construction methods which promote good drainage and rapid drying
The goal of foundation moisture management is to construct the basement, crawlspace, or slab in a way that keeps moisture from getting in in the first place
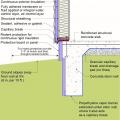
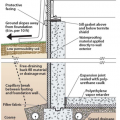
This exterior insulated slab-on-grade monolithic grade beam foundation is protected from pests by termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, brick veneer over slab-edge insulation, and rock ground cover.
This house with an insulated slab is protected from pests with a termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, insect screen covering bottom of furring air gap, and brick veneer over slab-edge insulation
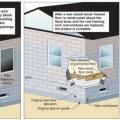
This left-to-right sequence shows the method of wall extension to flood-proof a masonry house on a slab foundation. Here the new, raised floor is wood-framed over a wet-floodproofed crawlspace, but using fill to create a new raised slab is also an option.
This plumbing pipe is wrapped with a stainless steel mesh skirt that is clamped to the pipe before the concrete slab is poured to to keep out bugs and rodents
This raised-slab CMU and brick foundation includes flood-resistant features such as a sloped grade, capillary break under the slab (gravel or sand), vapor barrier under the slab (polyethylene sheet), and capillary break at the top of the foundation wall
This raised-slab poured concrete foundation includes flood-resistant features such as a sloped grade, capillary break under the slab (gravel or sand), vapor retarder under the slab (rigid insulation), and capillary break at the top of the foundation wall
Wrong – Drain pipe has been cut and foundation penetration has not been properly sealed