Showing results 1 - 23 of 23
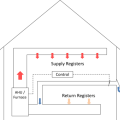
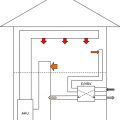
A central fan-integrated supply system uses a fresh air intake ducted to the home's central furnace or air handler unit to supply fresh air throughout the home
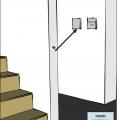
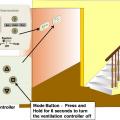
A ventilation controller with a manual override is located on a central air handler fan that is located in an accessible location
Continuously-operating ventilation & exhaust fans include readily accessible override controls
Exhaust fan installed but in wrong direction causing excessive bend and duct is uninsulated
If integrating an ERV/HRV with the heating/cooling duct system, add dedicated ducts for either the supply or return side to prevent short-circuiting of air distribution
In this ventilation configuration for a multifamily building, outside air enters through a dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS), and inside air exits the space through bathroom and kitchen exhaust fans
Lower-cost local ERVs are usually installed in a ceiling to supply outdoor air to and exhaust air from the room in which they are located
Rater-measured ventilation rate is within 100-120% of HVAC contractor design value (2.11)
Right - Each individual unit in this multifamily building has its own energy recovery ventilator (ERV) to provide balanced ventilation to the dwelling
The ventilation controller is next to the thermostat and has a manual override button
This bath exhaust fan ventilation control can be set by the HVAC technician for continuous operation, delayed shut off, or a set amount of minutes each hour
This central ventilation system uses an energy recovery ventilator, pre-conditioning unit, and elevator shaft exhaust fan to supply air to dwelling units and corridors and to exhaust air from units and the elevator shaft in a multifamily building
This energy recovery ventilator (ERV) provides balanced ventilation to a dwelling unit in a multifamily building