Showing results 1 - 20 of 20
A portable power meter shows the power usage of equipment; e.g., this laptop is drawing 12 watts while idle
A roof-mounted solar electric system can be sized to produce enough electricity to power the home and an electric car.
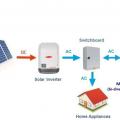
Basic layout diagram of an AC-coupled solar battery system with a Grid-tied (hybrid) setup
Cooling setting adjustments on a refrigerator allow the unit to be tuned to meet the target temperature for energy efficiency
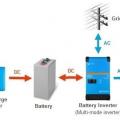
Example of a basic layout for a DC-coupled off-grid solar battery system using a MPPT solar charge controller
Incandescent lights such as these are a wasteful consumer of generator or battery energy, producing much more unwanted heat than light
LEDs cut energy costs by using less watts to produce the same amount of light as other light sources.
Portable gasoline-powered generators like this one can power smaller emergency cooling and refrigeration loads
Right – A utility room provides adequate space for the home’s mechanical systems and electronic smart home monitoring equipment.
Right – Batteries can extend the hours of power the home’s PV panels can provide.
Right – Space was provided next to the electric meter for home’s solar and home energy management tracking electronics.
Right – The PV system inverters and battery take up minimal space in the garage.
Right – The solar system production is tracked next to the home’s electrical meter.
Right – This home solar system includes batteries that provide power during peak evening hours.
The Lighting Facts label helps consumers select light bulbs based on brightness, energy cost, lifetime, color, and energy use.
These two battery storage modules are charged by a 6 kW solar PV system during daytime hours and provide 27 kWh of whole house backup electricity storage
This infrared image shows little heat gain from north-facing double-pane windows with blinds, but significant heat output from computer monitors
This larger, less efficient refrigerator shows a listed amperage of 6.5 A, which indicates that it draws 780 watts (6.5 A x 120 V)
Wrong: Electrical components were installed near ground level and are likely to be flood damaged.