Showing results 1 - 100 of 422
Right - Drywall is installed as an air barrier above the central hallway duct chase prior to installing the trunk ducts.
A constant airflow regulator is a modulating orifice that automatically regulates airflows in duct systems to constant levels
A constant airflow regulator is fitted into the neck of the supply duct to control air flow to deliver the design airflow regardless of pressure variations
A duct leakage test is performed on a ducted heat pump system using a duct tester (blower fan) and a digital manometer.
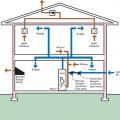
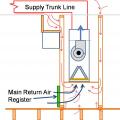
A ducted central return brings air from central return registers back to the air handler through insulated, air-sealed ducts
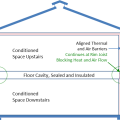
A floor cavity between the first and second floor can provide a conditioned space for HVAC ducts if the rim joists are insulated and air sealed, if sufficient space is available, and if open-web floor joists are used
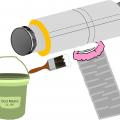
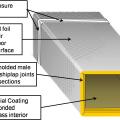
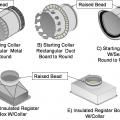
A nylon draw band and tensioning tool are used to secure the inner coil of the pre-insulated flexible duct
A nylon draw band and tensioning tool are used to secure the inner liner of the pre-insulated flexible duct
A second layer of rigid insulation is installed over the 2 in. by 4 in. retaining strip
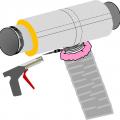
A technician assembles the spray sealant injection system to seal HVAC ducts from the inside
A triple-filtered energy recovery ventilator is installed with individual supply ducts to provide fresh air to each room.
After securing the inner coil, cover the draw band and the seam with a generous amount of mastic
Air handler platforms used as return air plenums can draw air from vented attics and crawlspaces through other connected framing cavities
Air seal a heat pump or air conditioner air handler cabinet at all seams, holes, and junctions
Air seal all holes and seams in the furnace cabinet with mastic, foil tape, or putty
Air seal and insulate flex ducts
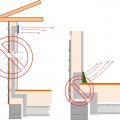
Air seal around all duct shafts and flues installed through ceilings, walls, or flooring to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air seal duct boot to ceiling by installing fiberglass mesh tape and mastic over seam
All of the ductwork for the efficient (8.5 HSPF, 15 SEER) heat pump is mastic sealed and installed in conditioned space.
All other supply ducts and all return ducts in unconditioned space have insulation ≥ R-6
An energy recovery ventilator provides filtered fresh air to every room in the house.
An in-line airflow station installed in rigid duct provides a location to measure ventilation airflow
Back-draft damper still has a piece of tape that prevented it from rattling during shipping
Because this ICF and spray foamed house is so well insulated, the HVAC system is smaller, the round metal ducts are smaller diameter, and the duct layout is more compact.
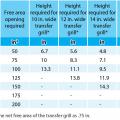
Bedrooms pressure-balanced and provide 1 sq. in. of free area opening per 1 CFM of supply air or achieve a Rater-measured pressure differential ≤ 3 Pa
Bedrooms pressure-balanced and provide 1 sq. in. of free area opening per 1 CFM of supply air or achieve a Rater-measured pressure differential ≤ 3 Pa
Building cavities not used as supply or return ducts unless they meet Items 3.2, 3.3, 4.1, and 4.2 of this Checklist
Buried ducts are laid on the floor of a vented attic then covered with spray foam and blown attic floor insulation
Cavity used for return is not insulated and is not air sealed, which will pull in air from outside
Closed-cell spray foam covers the heat recovery ventilator ducts and also seals all top plates and seams in the ceiling drywall of the vented attic.
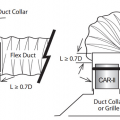
Collars that are specifically made for flexible duct have a raised bead to prevent the duct from slipping off
Connect the plastic application tunnel from the injection equipment to the supply plenum.
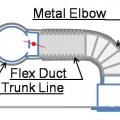
Consider using a metal duct elbow instead of flex duct at boot connections to prevent compressions
Coordinate with other trades including framers, plumbers, and electricians to prevent needless looping of flex duct
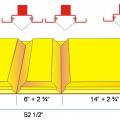
Cut fiber board with a red V-groove tool and a gray shiplap tool to create mitered corners and a shiplapped edge for duct sections
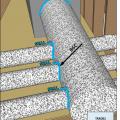
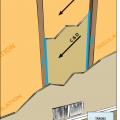
Cut-away view showing unsealed gaps around a heating duct that goes through a wall
Door has been undercut to allow for specified amount of air flow therefore contributing to pressure balancing
Drywall is installed before framing in dropped soffits to provide an air barrier above these duct chases.
Duct boot is air sealed to ceiling by covering the seam with fiberglass mesh tape and mastic
Duct boots sealed to floor, wall, or ceiling using caulk, foam, mastic tape, or mastic paste
Duct lacks adequate support to carry the weight so the few straps are pinching the duct
Duct to boot connection of jump duct not fastened and sealed
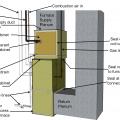
Duct/pipe penetration with metal cap flashing and wood blocking for trim attachment
Ducts are insulated but strapping is compressing the insulation therefore reducing the R-value
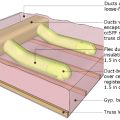
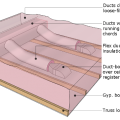
Ducts running parallel to trusses have limited width due to truss spacing
Ducts sagging because supports not installed at regular intervals
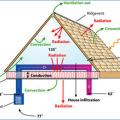
Ductwork located in a vented attic is subject to high attic temperatures and significant heat gain through the walls of the ducts
Electronically controlled dampers allow this central air system to provide zoned heating and cooling to specific parts of the home.
Example of an HVAC installer’s balancing report form