Showing results 1 - 100 of 167
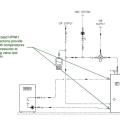
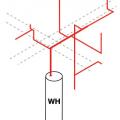
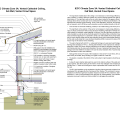
Right: dedicated tank connections for HPWH inlet and outlet provide hydraulic separation
These folding louvered porch doors provide effective shade from low-angle east and west sunlight and can open for views; the photovoltaic panels overhead allow in filtered natural light
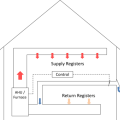
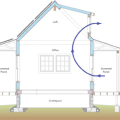
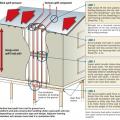
A central fan-integrated supply system uses a fresh air intake ducted to the home's central furnace or air handler unit to supply fresh air throughout the home
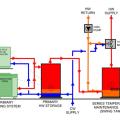
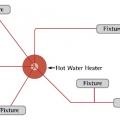
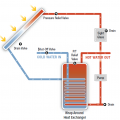
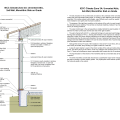
A central heat pump water heating system with a temperature maintenance swing tank configuration uses the water from the primary storage tank to provide most of the heat for hot water circulation temperature maintenance
A direct-vent sealed-combustion fireplace takes its combustion air directly from outside through a dedicated air inlet and vents combustion products directly outside
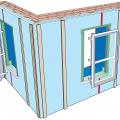
A flanged window unit is installed with straps that fasten to the interior surfaces of the plywood extension box; furring strips on each side of the window will be attached after the flanged window is installed and flashed
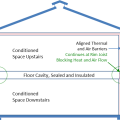
A floor cavity between the first and second floor can provide a conditioned space for HVAC ducts if the rim joists are insulated and air sealed, if sufficient space is available, and if open-web floor joists are used
An exhaust fan pulls damp air out of a retrofitted sealed crawlspace while drawing in dry air from the living space
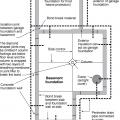
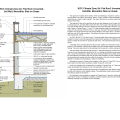
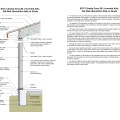
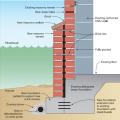
Basement plan showing sump pump location and perimeter drain that empties to the sump pit
Before sealing and insulating the crawlspace, the windows were sealed, the window wells backfilled, and sumps pumps were installed that discharged to the gutter downspouts
Braced cripple wall construction in crawlspace anchored to framing and foundation
Building Science Corporation used convection to help cool this structural insulated panel (SIP) cottage in Georgia.
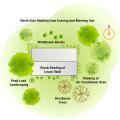
Careful landscaping can preserve roof-top solar exposure and provide shading to help control solar gain through windows.
Clerestory windows bring light in from above, reflecting it off of surfaces, making it more appealing than the direct light that comes from skylights
Climate-specific features include bug- and moisture-resistant concrete block construction and borate-treated interior framing; a hurricane-resistant spray-foamed hip roof; and ventless roof soffits to keep out wind-driven rain.
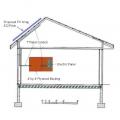
CPVC fire sprinkler piping is insulated using the tent method, as described in NFPA 13D.
Create defensible space against wildfires by limiting fire fuels in the immediate, intermediate, and extended zones around the home
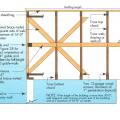
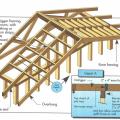
Critical connections for providing a continuous load path in buildings and storm shelters
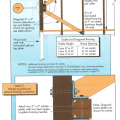
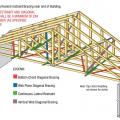
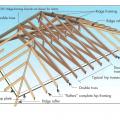
Example A of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example B of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example of a truss bracing requirement tag that some truss manufactures place strategically onto the truss to remind installers
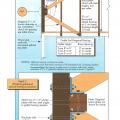
Example sketch of porch for calculations showing tributary areas for column uplift loads
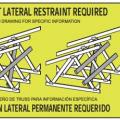
Example truss bracing for resisting wind loads as determined by design software used by truss manufactures
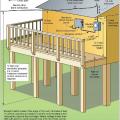
Exterior electrical service components are raised and clearances are provided around components to minimize contact with flood waters and people
Exterior shading devices such as awnings or overhangs can significantly reduce cooling loads
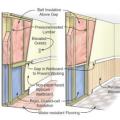
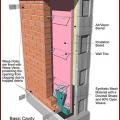
FEMA recommends techniques like open lower wall cavities with exterior rigid foam insulation and paperless drywall for flood-resistant, dryable wall interiors.
Furring strips provide a mounting surface for siding over the smart house wrap membrane which serves as a drainage plane over cork insulation installed on the exterior of this home.
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
Infrared photometry shows the impact of a roof overhang on the south façade of a home, where the unshaded patio stonework is significantly hotter than the shaded portions of the patio and wall surfaces (temperature scale shown is in Celsius).
Key connection points for a continuous load path for earthquake and high wind disaster resistance
Light-colored roofs and walls and deep overhangs for shade are some of the features used by builders in the hot-humid climate (Source: Alys Beach Construction).
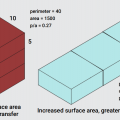
Low perimeter to area (P/A) ratio home designs reduce heat transfer and perform better in hot climate zones than high P/A ratio homes.
Multi-layer honeycomb cellular shades such as these can provide summertime energy savings by blocking and reflecting solar heat, as well as wintertime energy savings by providing added insulation.
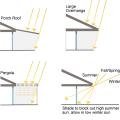
Porch roofs, pergolas, and large overhangs can effectively shade windows and doors facing south, southeast, southwest, or even due east or west for most of the day if the overhang is very deep and sufficiently wide.
Research by the Florida Solar Energy Center showed that light-colored and reflective roofs reduced cooling energy consumption by 18%-26%, reduced peak energy demand for cooling by 28%-35%, and reduced attic temperatures by 20°F.
Right - All seams in the HVAC equipment and ductwork are sealed with mastic; because the HVAC equipment is in the garage, it is an air-sealed closet.
Right - Dovetail-shaped plastic mesh is installed to collect mortar droppings at the base of the wall to keep weep holes from being clogged.
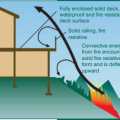
Right - Roofs with simple geometries are less susceptible to ignition from wind-borne embers getting lodged on the roof in a wildfire.
Right - Skylights provide natural light while maintaining privacy in a narrow second-story bedroom.
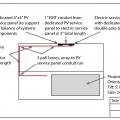
Right - Solar photovoltaic panels are installed on the highest parts of the roof to avoid being shaded by other parts of the house.
Right - The simple rectangular design of this home provides a large expanse of roof for solar panels.
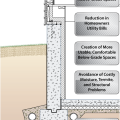
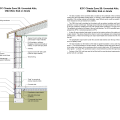
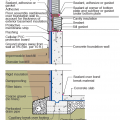
Right - This concrete basement wall has exterior rigid insulation and comprehensive moisture management details.
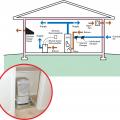
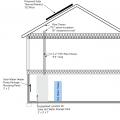
Right – A builder of a DOE Zero Energy Ready certified home explains how a central manifold distribution system with PEX piping works.
Right – A mall crew with a crane can assemble a home of structural insulated panels (SIPs) in just a few days.
Right – A simple stacked rectangular design and well-insulated and air-sealed ICF walls provide for an extremely energy-efficient structure.
Right – Even house wrap is installed in the factory for these modular homes where each floor is factory assembled.
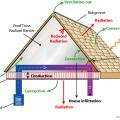
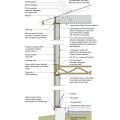
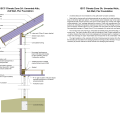
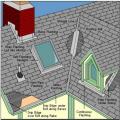
Right – Flashing is installed around chimney, skylight, vents, dormers, in valleys and at eaves
Right – Horizontal overhangs on this house block sunlight in the summer while allowing it in during winter
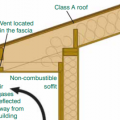
Right – In wildfire prone areas, using a flat soffit with venting on the fascia instead of an angled soffit with down-facing venting reduces the risk of catching rising embers.