Showing results 1 - 50 of 147
A 5,000- 6,000 Btu/hr air conditioner drawing about 500 watts can be installed in one window of a designated cool room (it is important that the installation is insulated and well-sealed
A battery storage system can provide reliable back-up power during a grid power outage
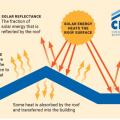
A cool roof utilizes materials with high solar reflectance and thermal emittance to reflect solar energy and reduce heat gain to the home
A cool room should have low enough heat gains to be easily cooled by a small single-zone cooling system such as a mini-split or a window air-conditioner as shown here
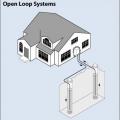
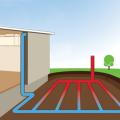
A ground source heat pump with an open-loop piping system using vertical injection and recharge
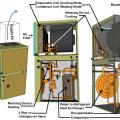
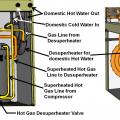
A ground-source heat pump has the same components as a standard air-to-air heat pump except that the liquid-to-refrigerant heat exchanger coil is located inside rather than outside
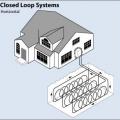
A ground-source heat pump with a closed-loop horizontal “Slinky™ “piping arrangement
A mini-split air-conditioning system can be a highly effective low-energy approach to provide cooling to one designated zone in the house
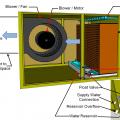
A modern single-inlet direct evaporative cooler draws outside air through an 8- to 12-inch media filter
A properly sized cold climate heat pump can meet 100% of a home’s heating load in nearly any location in the United States
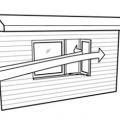
A reversible window fan can operate via thermostatic or remote control and can selectively exhaust air or bring in outdoor air
A screened-in porch will protect windows from rain, provide shade, and allow more airflow through windows than window screens would
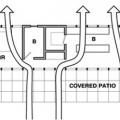
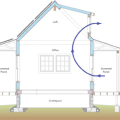
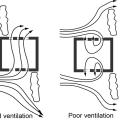
A shallow, open floor plan allows free flow of cross ventilation through the house
A variety of battery-powered fans can be used for a cool room without electric power; most charge off a USB charger so they can be solar charged
Air seal a heat pump or air conditioner air handler cabinet at all seams, holes, and junctions
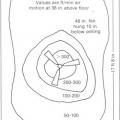
Air speeds generated by a typical ceiling fan are in the ideal range for providing occupant cooling without causing disruption
Airflow can be directed across thermal mass in the ceiling, floor, or elsewhere inside the home through various window and louver configurations
An innovative U-shaped heat pump offers SEER 15 efficiency and operation with smart phones
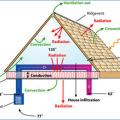
Building Science Corporation used convection to help cool this structural insulated panel (SIP) cottage in Georgia.
Ceiling fans can be used to aid a night flush strategy by helping to cool down wall and floor surfaces more thoroughly at night, and by providing comfort ventilation during the day
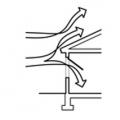
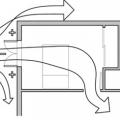
Comfort ventilation focuses on airflow over occupants; in this example of wind-driven cross ventilation, the air is directed through the main occupied areas of the bedroom
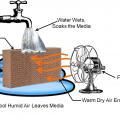
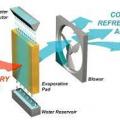
Concept behind an evaporative cooler – warm air is cooled as the air passes through a wet medium and gives up some of its heat to evaporate the water
Cool towers like this one at the Zion National Park Visitor Center can provide cooling to a building without any energy consumption
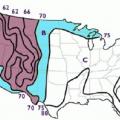
Cooling air temperatures that can be achieved by a direct evaporative cooler at various outdoor conditions
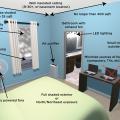
Create a cool room to shelter from extreme heat by selecting a room in the basement or on the north or shaded side of the house, air sealing and insulating, providing low-wattage and battery-operated cooling, and reducing interior heat loads.
Deep overhangs and porches provide midday shade for most of the windows on this home in Albuquerque, NM.
Dense hedges can encourage cross ventilation (left image) or not (right image) depending on how they are placed relative to windows
Double fan window units can have multiple operational modes; most often outdoor air will be brought in at night when outdoor conditions are cooler
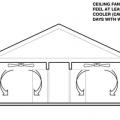
Ducted whole-house fans should be installed with the duct curved and the fan suspended from rafters to reduce noise and vibration transmission to the living area.
Ductless indoor units like this one are controlled individually by handheld remote controllers.
Ductwork located in a vented attic is subject to high attic temperatures and significant heat gain through the walls of the ducts
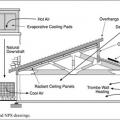
Earth tubes buried in the ground can provide pre-cooling of ventilation air or primary cooling if designed deep and long enough
ENERGY STAR-rated ceiling fans and openable windows oriented to prevailing summer breezes help provide low-cost cooling.
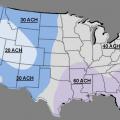
Evaporative Cooler Sizing in ACH based on wet-bulb temperatures at 1% summer design conditions
Evaporative coolers use a fan to draw outside air through a wetted pad which cools and humidifies it
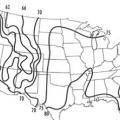
Evaporative cooling is most appropriate in areas where the summer design mean coincident wet bulb temperature is less than 70°F, shown in purple here and labeled as region “A”
Even when wind is blowing parallel to a wall, an open casement window can create a zone of higher pressure near the window opening, driving airflow into the house
Example expanded performance table from a 1.5-ton air conditioner
Example of an earth-sheltered home in hot climate Tempe, AZ uses the cooling properties of the ground to decrease cooling costs