Showing results 1 - 20 of 20
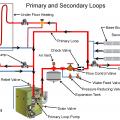
A boiler system can be set up with primary and secondary loops to supply hot water for multiple uses
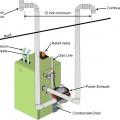
A Category I induced draft boiler uses an induced draft fan to pull air through the combustion chamber and to the flue
A direct-vent sealed-combustion fireplace takes its combustion air directly from outside through a dedicated air inlet and vents combustion products directly outside
A direct-vent sealed-combustion furnace has dedicated pipes for combustion air and exhaust
Because flue temperatures are cool, intake and exhaust ducts on a Category 4 direct-vent sealed-combustion condensing furnace can be made of PVC
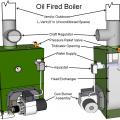
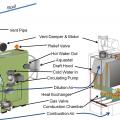
Category III oil-fired, sealed-combustion boiler configured as a direct-vented appliance that draws its combustion air from outside
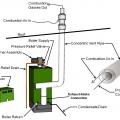
Category III oil-fired, sealed-combustion boiler with the burner assembly cover removed
For fireplaces that are not mechanically drafted or direct-vented to outdoors, total net rated exhaust flow of the two largest exhaust fans is .15 CFM per 100 sq. ft. of occupiable space when at full capacity
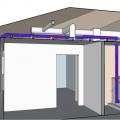
Furnaces, boilers, and water heaters located within the home’s pressure boundary are mechanically drafted or direct-vented
In a Category I gas-fired, natural-draft boiler, the natural draft of the heated flue pulls combustion air through the draft hood into the combustion chamber
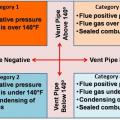
National Fuel Gas Code (NFPA 2012) identifies four categories for combustion furnaces and water heaters based on combustion type (sealed or unsealed) and vent pipe temperature
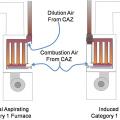
The natural draft and induced draft furnace are both Category I appliances that receive combustion air from the combustion appliance zone
The raised hood at the base of the vent stack on this water heater shows that it is an atmospheric vented gas water heater