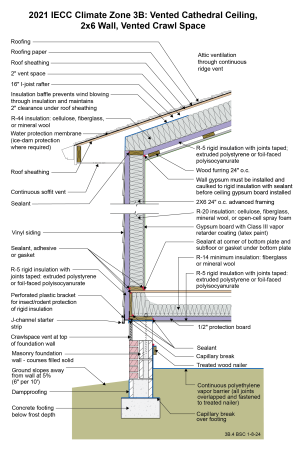
Notes
Drawing 3B.4: IECC CZ 3B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
- The rigid foam installed above the ceiling is not necessary to meet energy efficiency code or to control vapor. Instead, it is used to allow the creation of a service raceway between the rigid foam and the gypsum board below it. The rigid foam acts as the air control layer instead of the gypsum board. The service raceway allows the air control layer to be undisturbed by the electrical penetrations in the ceiling. This approach also reduces drywall cracking. From a code standpoint, however, the rigid foam and the raceway are not required, and R-49 fibrous cavity insulation could be installed directly on top of the gypsum board.
- This wall has no structural sheathing. Instead, it has metal bracing (not shown) for racking resistance.
- The rigid foam on the exterior of the wall is not necessary to meet energy efficiency code or to control vapor. It allows construction without using structural sheathing. Alternative methods of wall bracing are used instead (for example, metal strapping, not shown), and the rigid foam provides a backstop for the cavity insulation as well as some structural support to the siding. Many contractors have found this to be a more economical approach. It is possible to simply use well-installed house wrap instead of the rigid foam, but this would require siding that can span between studs without intermediate backing. Another option for this wall would simply be to use structural sheathing (OSB or plywood) in place of the rigid foam, with house wrap on the exterior of the sheathing.
- The wall is framed with 2x6 24” o.c. advanced framing as it uses less board footage (volume of wood framing) than standard 2x4 16” o.c. framing and therefore is less expensive in material cost. It is also less expensive in labor (25% fewer framing members) and is faster to assemble. Although the code allows for 2x4 framing and lower R-value cavity insulation, the use of advanced framing and the associated cost savings more than offset the increase in the cost of cavity insulation (this of course depends on relative price fluctuations in labor and materials).
- Although the minimum R-value of the insulation in this wall is R-13 per IECC, fire code may require the entire cavity to be filled, likely resulting in a higher R-value for a 2x6 wall.
- The plastic L-bracket at the bottom of the wall’s exterior rigid insulation should be perforated to facilitate drainage.
- A class III vapor retarder (latex paint) is used on the interior surface of the walls and ceiling instead of a vapor barrier. This allows drying to the interior. Avoid vinyl wallpaper and oil-based paint or coatings in Climate Zone 3. These wall coverings are vapor impermeable and increase the risk of condensation within the wall.
- The R-5 rigid insulation on the underside of the floor framing prevents moisture from the vented crawlspace from damaging the floor framing and floor finishes. The combined R-value of the floor cavity insulation and the floor rigid foam insulation should be at least R-19 to meet IECC 2021. A minimum thickness of 1 inch is recommended for the rigid foam for constructability. The protection board is necessary to prevent rodents and other animals from damaging the assembly.